You are reading ChinaImportal's Newsletter!
IMPORTANT: If you don't see any images in this message, be sure to click the "Show Pictures" link in your email reader. Thanks!Follow on LinkedIn Follow on Google Plus Follow on Facebook

In this product guide, we explain everything you must know about Underwear & Lingerie Manufacturers in China, including industrial clusters, supplier qualification and design customization options. We also explain what you must know about potential quality issues and applicable labelling requirements – and substance restrictions in the United States and the European Union.
Underwear and Lingerie Manufacturing Clusters in China
China’s export oriented underwear manufacturers are largely concentrated in the country’s primary textiles production centers; Guangdong Province, Fujian Province and Zhejiang Province. If you intend to visit manufacturers in Mainland China, you are likely to find yourself in one of the following cities:- Quanzhou, Fujian
- Jinjiang, Fujian
- Shantou, Guangdong
- Guangzhou, Guangdong
- Dongguan, Guangdong
- Zhongshan, Guangdong
- Yiwu, Zhejiang
Qualifying Manufacturers
Underwear and lingerie is, in relative terms not a very capital intensive industry. Manufacturers in such ‘low value added’ industries then to be rather unsophisticated, thereby requiring a rigid Quality Assurance (QA) process, managed by the buyer.The first step of the QA process is, as explained below, to draft a comprehensive product specification. There are, however, certain useful signals for qualifying Underwear and Lingerie Manufacturers:
- Business Scope (As specified on the manufacturers business license)
- Registered Capital (As specified on the manufacturers business license)
- Substance Test Reports (i.e., REACH and Oeko Tex Standard 100)
- Quality Management System / Production Lines Audit Reports (i.e., ISO 9001:2008)
- Social Compliance Certification / Audit Reports (i.e., Sedex and BSCI)
- Environmental Audit Reports (i.e., ISO 14000 series)
What to Include in The Techpack
a. Design Drawing
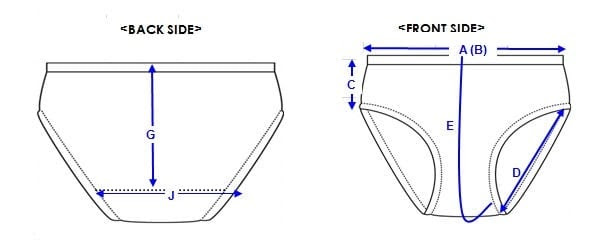
The product design can either be based on an existing ODM SKU, or an OEM specification. While you may submit, or submit, reference samples – they are only complementary to the design drawing. These are your options:
- OEM: Design drawing submitted by the buyer
- ODM: Design drawing submitted by the supplier
b. Reference sample
A reference sample is either provided by the supplier (when buying ODM products), or the buyer (when buying an OEM product). As mentioned, the reference sample is only complementary to, and not a replacement for, a design drawing.c. Fabric
The most straightforward method is to order fabric samples, or complete units, from the supplier. The buyer can then freely select the material of choice from the supplier’s standard catalog. Another method is to submit fabric samples, that the supplier can match with a fabric from their own standard catalog – or, in rare cases, weave the fabric entirely according to the specifications of the buyer.d. Size Table
The size table is an appendix of the design drawing, listing dimensions for each size. ODM products can also be customized by adjusting the size table accordingly. The size table must also be complemented with dimensional tolerancee. Labels
Underwear and lingerie are subject to general textiles labelling requirements. Said labelling requirements differs between markets, and buyers are unwise to assume that the supplier is aware of the specific requirements in your market. Hence, you must provide ‘ready made’ graphical files (.aiformat) to the supplier. Include the following:- Label dimensions (i.e., 15 x 30 mm)
- Country of Origin (required in the United States)
- Washing Instructions and/or symbols
- Batch ID
- Logo / Website
Quality Assurance
a. Common Quality Issues
Quality issues in textile manufacturing often stem from an incomplete or conflicting product specification. Below follows a list of common quality issues when buying Underwear and Lingerie:- Incorrect dimensions
- Incorrect component position (i.e., double fabric)
- Incorrect / low quality materials
- Incomplete seam lines
- Dirty and damages
b. Quality Control
The purpose of the quality inspection is to defect quality issues before the produce is packed and shipped. When buying Underwear and Lingerie from Chinese manufacturers, you must draft a Quality Inspection protocolincluding the following procedures:- Visual Inspection (i.e., Dirt, damages, seams and printed labels)
- Dimensions (i.e. Double fabric length)
- Fabric (i.e., Weight and Washing)
Compliance Testing
Underwear and lingerie are subject to various substance regulations in major markets, primarily the United States and the European Union. Depending on your market, you need to ensure compliance with one or more of the following:a. REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and restriction of Chemicals)
- Country / Market: The European Union
- Description: REACH restricts the content of restricted SVHC (Substance of very high concern) in textiles, and other consumer products, sold within the European Union. The list of SVHC includes hundreds of substances, including lead, cadmium and formaldehyde.
- Read more: REACH Compliance Explained: What Every EU Importer Must Know
b. California Proposition 65
- Country / Market: California, United States
- Description: California Proposition 65 restricts more than 800 substances in consumer products. Products must either be compliant (i.e., proven rid of all restricted substances), or labelled accordingly. If your company is based in California, or if you intend to sell to buyers in the state, you must ensure compliance.
- Read more: California Proposition 65 Compliance – What US Importers Must Know
c. FHSA (The Federal Hazardous Substances Act)
- Country / Market: United States (All states)
Description: FHSA restricts various substances classified as, for example, irritants or strong sensitizers. This includes, among other substances, formaldehyde – a substance used by some textile manufacturers. The full list of mandatory bans and restrictions are available on CPSC.gov.
Read more: Regulations, Mandatory Standards and Bans (www.cpsc.gov)
Starter Package
Are you looking for reliable suppliers in China? With us, getting started is easier than ever: Click here to learn more.Supplier Screening
Found a supplier on your own? Let us perform an Anti-Fraud Screening before you order: Click here to learn more.Importing Custom Designed Jewelry from China: A Complete Guide

In this Product guide, we explain what you must know about buying ODM (Private label) and OEM (Custom designed) jewelry from Chinese, and other Asian, manufacturers. Keep reading, and learn more about product development, sample production and production regulations, applicable to Jewelry. We also guide you through the various labelling and testing requirements.
Product Development Process
1. Jewelry Parts Selection
Most jewelry buyers opt for factory standard components, rather than OEM (custom designed) parts. Most suppliers can, directly or through subcontractors, offer extensive jewelry part catalogs. Hence, you have the following options when designing your products:I. ODM Products (no design changes): Base your design entirely on the supplier’s existing ODM designs
Customize an existing ODM Product: Modify an existing ODM product by adding or removing parts (i.e., custom designed labels).
II. Custom Design (using ODM parts): Jewellery can be designed ‘from scratch’ using existing ODM parts from the buyers catalog.
III. Custom Design (using OEM parts): Custom designed parts results in high tooling costs, especially when buying a large number of SKUs.
Product documentation must be prepared for each SKU. Making jewelry samples require attention to detail, and key specifications are easily lost in translation. In order to reduce the risk of an endless number of sample batches, prepare the following for all SKUs:
- 2D Design Drawings (showing ODM parts and position)
- ODM Parts List
- ODM Parts Material Specifications
- Label / Logo Badge and Part Files (.ai format)
2. Pre-Production Samples
Option A: Self Assembled Jewellery Samples
If you intend to design your own jewelry using ODM parts, you might consider buying said parts directly from the manufacturer, rather than assembled samples. This approach can save weeks, and enable you to test new designs in a highly cost efficient way.The Self Assembled Samples shall then be returned to the suppliers, acting as Pre-Production Samples. However, make sure to order two sets of jewelry parts as you need to keep at least one piece of each SKU for your own reference.
Option B: Supplier Assembled Jewellery Samples
If you on the other hand intend to base the design on the supplier’s existing ODM samples, you should buy assembled samples, rather than ODM components. This also enables you to test the supplier’s attention to detail. However, the samples are only as good as the sample documentation. As explained in this guide, you shall expect several sample revisions before you are ready to place a first mass produced batch.3. Mass Production and Quality Assurance

A. Incoming Materials & Parts Inspection
Purchasing parts and materials is the first step of the production process. As quality issues, when manufacturing jewelry, tend to stem from the production of the parts, rather than the later assembly stage, you shall consider hiring an inspector as soon as the parts arrive at the factory. Hence, quality issues can be avoided at an early stage, thereby reducing the risk of severe delays.B. Pre-Shipment Inspection
The final, and most important, inspection shall be carried out when the products are fully assembled. Some defects, for example scratches, occur during assembly and packaging, thereby making the final, pre-shipment inspection, essential when importing jewelry from China. However, as always, clear instructions are the key to a successful outcome. Provide the quality inspection agency with all design drawings and component lists well in advance of the inspection date.Product Regulations and Compliance Testing
1. Applicable Regulations
Jewelry is subject to various substance and ‘mechanical’ regulations in the United States, the European Union and other markets. Jewelry made for children younger than the age of 12 is also classified as a children’s product, and is therefore subject to additional regulations. The table below explains what jewelry imports in the US and EU must know:| Market | Regulation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| US | CPSIA |
The Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act (CPSIA) regulates all toys and other children’s products imported to, or made in, the United States. Visit this link to read more about importing Children’s Jewellery to the United States.
|
| US | CA Prop 65 |
California Proposition 65 restricts more than 800 substances in consumer products. Unlike CPSIA, which only applies to Children’s jewellery, California Proposition 65 also applies to jewelry sold to adult. Compliance is mandatory if you intend to sell in, or to buyers in, California and employ at least 10 workers. However, even if your total number of employees is less than 10, most (online and offline) retailers still require compliance with California Proposition 65.
|
| EU | REACH |
REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and restriction of Chemicals) restricts content of SVHCs in all consumer products sold in the European Union. Compliance is mandatory for all Jewellery imported to the EU.
|
| EU |
EN 14682:2007
EN 71 Part 1
|
EN 14682:2007 (Safety of children’s clothing. Cords and drawstrings on children’s clothing specifications) and EN 71 Part 1 restricts cord and chain length to prevent strangulation. Click here to read more.
|
| AU/NZ | AS/NZS ISO 8124.1:2002 |
AS/NZS ISO 8124.1:2002 regulates children’s products sold in Australia and New Zealand, including jewellery marketed to children aged 14 or younger. Click here to read more.
|
2. Hallmarking and other Labelling Requirements
Platinum, Silver and gold jewelry are subject to Hallmarking requirements. Many countries have their own specific Hallmarking standards. Customs authorities are prone to checking imported precious jewelry, and improperly marked precious jewelry is likely to be seized.Apart from Hallmarking, which doesn’t apply to non-precious jewelry (i.e., stainless steel and pearl jewelry), country of origin markings may apply.
3. Compliance Testing & Certification Requirements
Whether or not compliance testing is mandatory depends on the market and the applicable regulation / directive. Compliance testing and certification is normally mandatory when importing Children’s Jewellery. However, even when testing is not mandatory, compliance always is. Hence, the question of whether or not your company shall submit samples for testing is often a matter of risk management.It’s also a matter of costs. Testing companies charge based on the number of samples. A necklace, for example, can consist of 5 to 10 different components and thereby result in very high testing costs.
The testing cost per SKU can range from $100 to $800, depending on the regulation and the number of different parts. Testing an entire Jewellery collection is therefore very costly. There are, however, a few strategies that can help you reduce the testing costs:
- Use the same Jewelry parts on as many SKUs as possible. Thereby, you reduce the number of lab tests needed to verify compliance.
- 2. Avoid Children’s Jewelry as the compliance testing requirements are very strict.
Recommended Jewelry & Accessory Trade Fairs in Mainland China and Hong Kong
Global Sources Fashion Fair
- Location: Hong Kong
- When: October 2015
- Official Website: Click here
HKTDC Hong Kong International Jewellery Show
- Location: Hong Kong
- When: March 2016
- Official Website: Click here
Canton Fair Phase 2
- Location: Guangzhou
- When: October 2015
- Official Website: Click here



No comments:
Post a Comment